

Urdu is a very popular language of the subcontinent , second only in the number of speakers to Hindi. It is the national language of Pakistan and an offical language of UP in India . It is the language of poetry and of literature .
You may freely copy these lessons for non commercial uses on to your web site , add sound files or modify them in any way you want - but please do mention Ukindia in them. .All these Urdu lessons on a floppy disk and a Learn to Read Urdu book by Balaji books and a cassette of nearly all the words and phrases and some songs on the lyrics page is available . Send your cheque-total $50 (£25 in UK ) for all items to Ukindia , P.O .Box 346 Nottingham UK , NG85FX . Allow 4-6 weeks for delivery. Send an email at the same time to ukindia
To get to a particular lesson change the address in your browser window . For example change zurdu1.htm to zurdu12.htm to get to Lesson 12 etc.
This is the most important lesson so once again do it very slowly and carefully and the rest of the 20 or so lessons will then seem very easy .
Each sound is represented by a letter . For example lets look at the letter K and N in in the next figure.

If for example you look at the figure below, K on its own is on your extreme right marked detached . If it occurs in the beginning of a word as in the word Kill it is written as in the next one along -ie its inital form marked 2. If it occurs in the middle of a word eg luKy it is written in the medial form 3 and if it occurs at the end of the word as in ducK it is like the 4th final form to your extreme left.
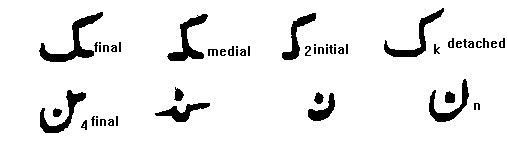 .
.
The above figure has the detached , initial . medial and final forms of K and N. You may have noted that the detached and final form form are usually very similar.
Note again that the detached form is on your extreme right then the initial , medial and final.
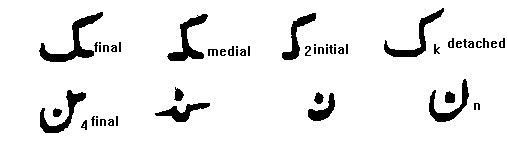
We would take the intial form of K marked 2 in the figure above and the final form of N marked 4 and join them together . Remember to read it R to L.
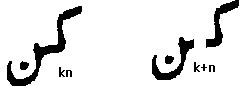 .
.
Easy isnt it ? .
Lets add some accent and vowel marks in between the letter K and N . Reading from the right of the screen the second word is k'n with the k pronounced a little longer since the accent mark (zabar) is over the k . The next word kn' has a longer n since the accent mark is over the n . The shapes of the vowels aa, i, ee, u , oo , o , au ,ae and aae are obvious from the figure and are explained in more detail after the figure .

Lets take our meaningless word kn and add vowel marks to it . The left word in the next figure reads kAAn ( ear). The AA is a vertical straight line. A vowel is not joined to the letter following it so the letter n in kaan is written in its detached form . Note also the slight change in the shape of K .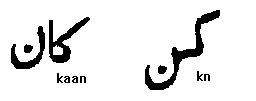
 .
. 
you may have to read it as 





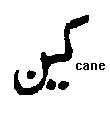
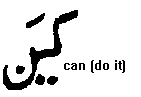

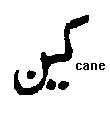

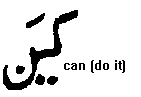





The vowel mark AA as we noted above is written as a straight vertical line. The next word to it on your left is kin . The vowel mark little i is a small slant line called in urdu ZER is placed BELOW the letter , in this case K. The next word on the second line is KEEN . Two dots are added to the little i - ZER- mark to make a big EE mark below the letter.
Then little u - KUN as in the word crook - the u mark -called PESH- is always above the letter ; next is big U -KOON as in sOOn - note you get a big fat worm like figure added to the little u-pesh- mark , but this worm is on level with the letter.

is O as in cone (icecream cone)- the worm on its own makes an O sound ; but when a zabar is added above the letter it makes an Au -KAUN (who in Urdu ) as in AUtumn . Note the difference between the words KOON and KAUN in the bigger figure above. . kOOn has a pesh on top of the worm while kAUn has a zabar on top of the worm.
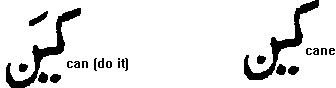
look again at CANE with the two dots marking the AE sound and the next figure to it CAN . We get the AAE sound in cAAEnada (Canada) by just adding a zabar at the top of the letter
The following are the vowel marks which modify the letters.

The madd , hamza and tashdid signs are special characters we will look at in the next lesson
Sometimes the letter N when it is the final letter is written without the dot in the middle and is not sounded except from the back of the throat as example in the word maa'n for mother.We shall look at this later.
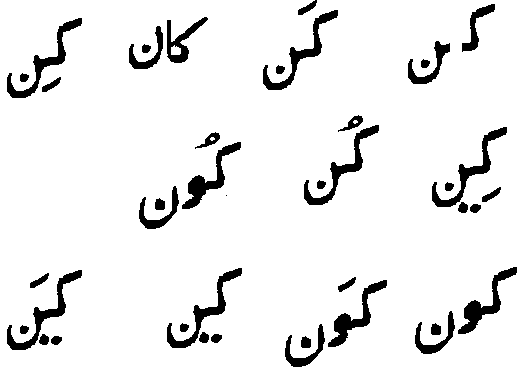
Here are the answers
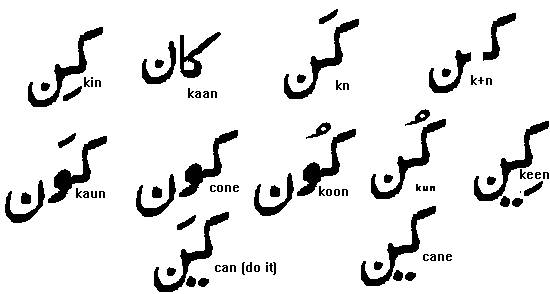 .
.
One important point to note is that the zabar mark and i mark called a zer are similar but the zabar is on top of a letter while zer which signifies i is below.